W Plot Diagram
The Nichols plot is a plot used in signal processing and control design, named after American engineer Nathaniel B. Nichols.[1][2][3]

The Plot, a platform game released in 1988 for the Amstrad CPC and Sinclair Spectrum; Plotting (non-fiction), a 1939 book on writing by Jack Woodford; Graphics. Plot (graphics), a graphical technique for representing a data set; Plot (radar), a graphic display that shows all collated data from a ship's on-board sensors.
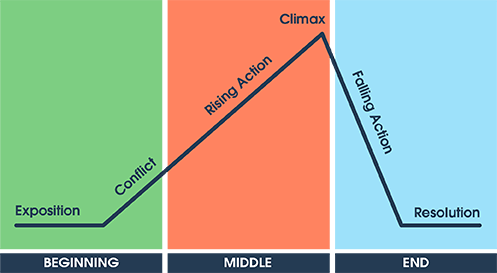
- Plot diagram is a schematic representation of the events that unfold in a story. The diagram does so with the help of a triangular or pyramid shaped drawing. When the events of a story are mapped in this way, the audience finds it easy to visualize the story’s key aspects.
- The Plot Diagram is an organizational tool focusing on a pyramid or triangular shape, which is used to map the events in a story.
- Plot diagrams allow students to pick out major themes in the text, trace changes to major characters over the course of the narrative, and hone their analytic skills. Lessons emphasizing these skills meet many Common Core Standards for English Language Arts (CCSS.ELA-Literacy).
Use in control design[edit]
Given a transfer function,
with the closed-loop transfer function defined as,
the Nichols plots displays versus . Loci of constant and are overlaid to allow the designer to obtain the closed loop transfer function directly from the open loop transfer function. Thus, the frequency is the parameter along the curve. This plot may be compared to the Bode plot in which the two inter-related graphs - versus and versus ) - are plotted.
In feedback control design, the plot is useful for assessing the stability and robustness of a linear system. This application of the Nichols plot is central to the quantitative feedback theory (QFT) of Horowitz and Sidi, which is a well known method for robust control system design.

In most cases, refers to the phase of the system's response. Although similar to a Nyquist plot, a Nichols plot is plotted in a Cartesian coordinate system while a Nyquist plot is plotted in a Polar coordinate system.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^Isaac M. Howowitz, Synthesis of Feedback Systems, Academic Press, 1963, Lib Congress 63-12033 p. 194-198
- ^Boris J. Lurie and Paul J. Enright, Classical Feedback Control, Marcel Dekker, 2000, ISBN0-8247-0370-7 p. 10
- ^Allen Stubberud, Ivan Williams, and Joseph DeStefano, Shaums Outline Feedback and Control Systems, McGraw-Hill, 1995, ISBN0-07-017052-5 ch. 17